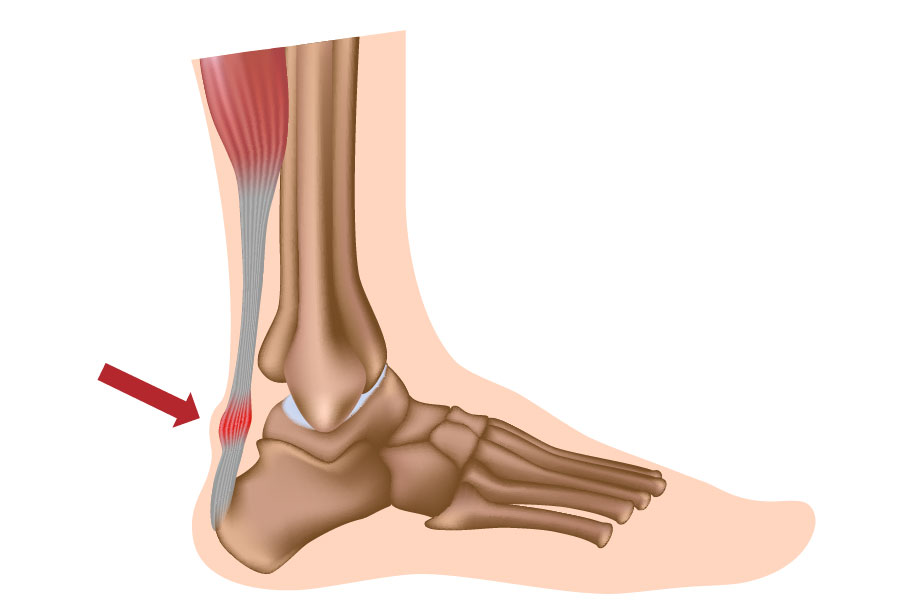
Achilles Tendon
The Achilles Tendon or its covering, the paratenon, is a common source of damage, pain or inflammation.
The tendon itself with long term repetitive trauma can undergo a degenerative process called tendinosis and in some cases can rupture completely.
There are many reasons for Achilles tendon problems including training regimes, tight calf muscles, or over-use. Abnormal over pronation is sometimes a mechanism for injury, or can delay resolution, due to the 'whipping' motion placed on the tendon.
A podiatrist assesses and treats any abnormal biomechanical strain placed upon the tendon, and can utilize electrotherapy such as Low Level Laser Therapy in treating Achilles tendon problems.

Arthritis
Arthritis is musculoskeletal disorder, which affects the joints, resulting in pain, stiffness and inflammation of the joints.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis treated?
We at The Footcare Centre focus our attention on two main areas
We achieve this by carry out one or more of the following:
Pressure Plate
Annual checks can be arranged utilising our pressure plate system that identifies the amount of force that is going through your skin and joints. This is used as a precursor to initiating insole/orthoses therapy once pressures reach a certain point.
Footwear
Correct footwear is key to keeping the rheumatoid foot intact by reducing pressures and keeping the foot stabilised so your podiatrist will advise upon this.
Simple Insoles/Orthotics
Simple insoles can be used purely as a way of offloading a particular joint/s to divert pressure away from the painful area which in turn can reduce the inflammation and ease walking.
An orthoses is a custom made device that is both functional (correcting the foot mechanics) and accommodative (offloading).
For persons with RA, hard or rigid orthotics generally causes too much pressure on the bone prominences, creating more pain. Therefore we use a particular orthoses that is made of softer yet controlling material.

Bunion
A bunion - called Hallux Abductovalgus - is the common name for a protruding big toe joint on the side of the foot which can cause difficulty finding shoes of sufficient width and can cause pain and rubbing.
A bunion is caused by a displacement of the first metatarsal bone (the long bone in the arch) and its connecting toe bone (called the phalanx). This displacement is oftentimes a result of poor footwear including fashion shoes, court shoes or pointed shoes.
The abnormal foot posture is also sometimes an underlying factor therefore a podiatrist may sometimes suggest correcting foot position or foot posture using orthoses (special insoles) as an adjunct to improving styles of footwear. Also there is often a tendency for bunions to run in families.
We also offer a wider fitting shoe service for help with difficult to fit feet

Corns and Hard Skin
Corns are dense local areas of hard skin which are caused due to recurrent pressure on the same area of skin. This is often caused due to abnormal biomechanics, foot deformities (such as hammer toes or bunions) or ill-fitting footwear.
Corns have a central core called a nucleus which under pressure is often very painful and requires treatment by a podiatrist. Treatment of corns will include the removal of the corn and will help address the abnormal pressure that is causing the corn to develop. Hard skin, or callus, however is caused by frictional forces or a more diffuse pressure area.
Hard skin can often be managed through filing or using a pumice stone and by using a foot moisturiser daily.
Diabetes
The above YouTube video is provided on our website for informational purposes only. Happy Feet does not take responsibility for its content and we are no way affiliated to the Ontario Ministry of Health.
This is a condition where you have raised blood glucose levels (called hyperglycaemia) due to a metabolic disorder.
Diabetes is directly linked with profound changes to your feet. The circulation to and around your feet can deteriorate meaning you are more susceptible to infection, less likely to heal quickly and your skin quality reduces meaning it is easier to damage. The sense of feeling in your feet can also reduce so that it is possible to damage your feet and not know about it.
Diabetes is directly linked with profound changes to your feet. The circulation to and around your feet can deteriorate meaning you are more susceptible to infection, less likely to heal quickly and your skin quality reduces meaning it is easier to damage. The sense of feeling in your feet can also reduce so that it is possible to damage your feet and not know about it.
It is important we monitor your feet regularly so that we can detect these changes early on.
You can see how even a seemingly simple problem like corns, callus or toenail cutting could cause much bigger problems under these circumstances.
Basic Guidelines for Diabetics
Warning Signs
Sports Injuries
Sports injuries of the foot, legs and knee or hip joints are common. These sporting injuries can be overuse injuries, acute trauma injuries or other chronic injuries.
Our podiatrists are able to assess the biomechanics of the way you walk and run in order to ascertain if the position and movements of the foot, leg, knee and hip are misaligned. If foot and leg posture or positioning is incorrect then the connective structures around all these joints are more likely to become injured through overuse.
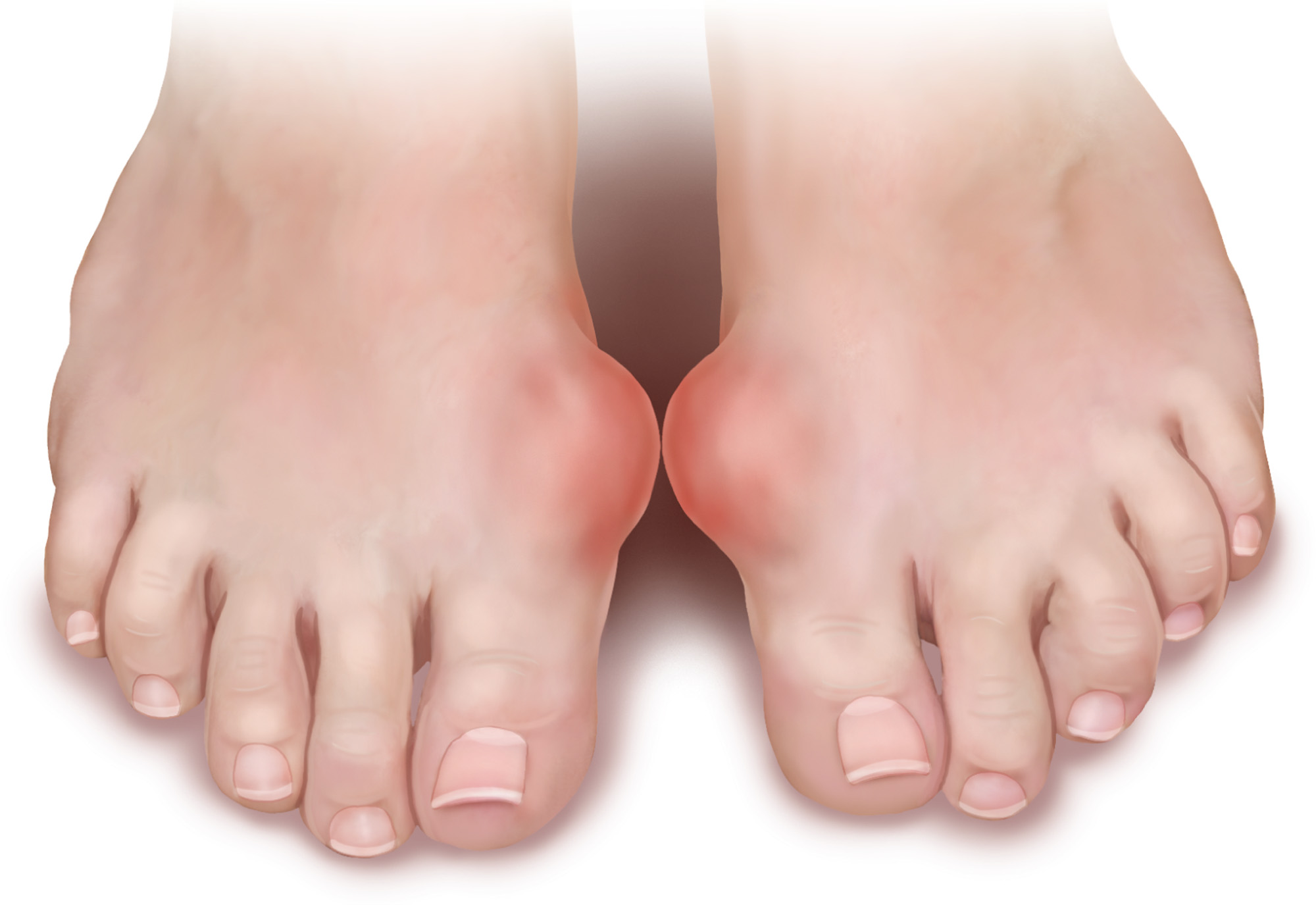
Gout
Gout is a metabolic disorder and results in the formation of Uric Acid crystals within joints. It is often larger joints that are affected, therefore in the foot the big toe joint is often seen as most affected.
Recurrent bouts of gout may cause arthritic change within a joint which your podiatrist can sometimes help manage through special orthoses (insoles) or footwear.
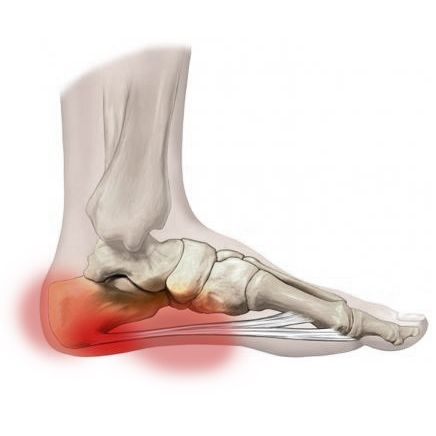
Heel pain (Plantar Fasciitis)
The plantar fascia is a fibrous band of tissue anchoring from the heel up along the arch to the toe joints. This commonly becomes inflamed - a condition known as plantar fasciitis. This is often due to the repetitive strain, called microtrauma, taken through this tissue over a period of time, which in turn causes long term damage and inflammation.
This condition can be treated by improving the biomechanics of the way you walk or run - thereby improving the way in which the foot and this tissue bears the strain placed upon it. Foot orthoses are specialised insoles that podiatrists often use in the treatment of this condition as well as addressing any muscle imbalances contributing to it.
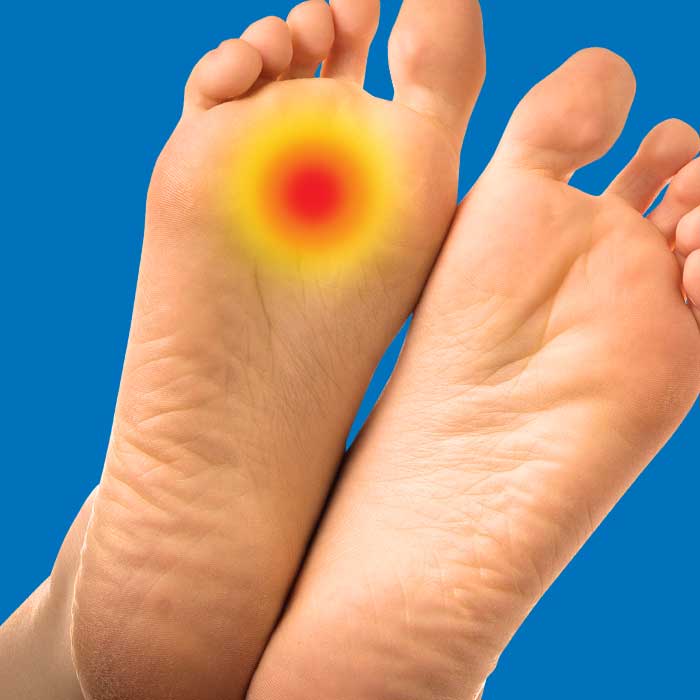
Metatarsalgia (Pain in the Ball of the Foot)
This is an umbrella term that describes pain in the metatarsal area of the forefoot. Abnormal pressure loading can be a common cause of pain in this area which can be attributable to footwear choices, foot posture (see biomechanics), reduction of the natural cushion made of fat and fibrous tissue under the ball of the foot or over-use.
Metatarsalgia treatment includes possible changes to footwear, cushioning or gel insoles, or even a detailed assessment of walking & foot and leg postures in order to prescribe specialised insoles called orthoses. In some instances referral for surgical management from a podiatric surgeon may be necessary.
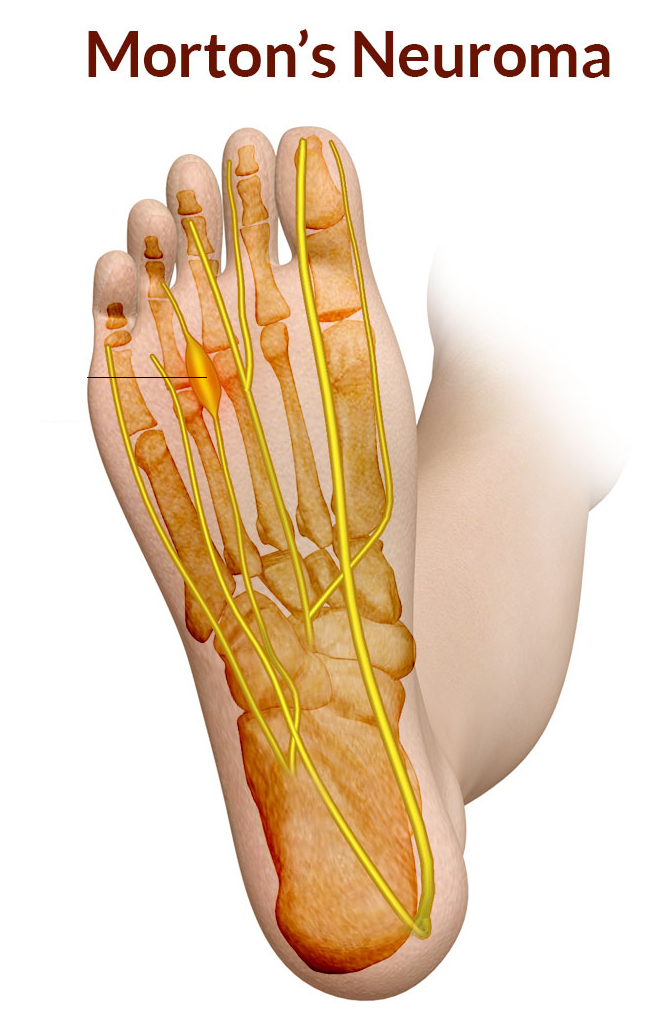
Mortons Neuroma
There are nerves in feet which run up towards the toes, finally branching off to give sensation into the toes themselves. Back at the level of the main toe joint, particularly between the 3rd and 4th toes, but also commonly between the 2nd and 3rd toes, these nerves are vulnerable to thickening.
This thickening which involves nerve, fibrous and vascular tissue is the result of the metatarsal bones, which run alongside the nerves, causing mechanical irritation to the nerve at the level of the main toe joint.
This mechanical irritation which predisposes people to neuromas is related to abnormal biomechanics, tight or compressive footwear.

Toe Joint Pain
A common change to a big toe joint is the condition Hallux Limitus. The abnomal compensations or foot postures that occur during walking can cause the big toe joint to jam up. Rather than moving like a hinge the big toe joint can become restricted by the way the foot is acting against the ground. This can slowly cause changes to the joint shape of the bones in the big toe joint, which results in a limitation in movement available at the joint. This is called a Hallux Limitus.
Hallux Limitus can be painful, and is often exacerbated by heeled shoes or activities requiring the bending of the big toe such as walking, bowling or golf. Hallux Limitus can also be caused following a trauma to the big toe or arthritis. Longer term a Hallux Limitus can progress to a Hallux Rigidus - whereby all the flexion is lost from the big toe joint and the joint becomes immobile.
Podiatrists are experts in treating this condition by ensuring the position and postures of the foot are corrected to ensure correct functioning of the big toe joint. This can be done through orthoses (special insoles) after assessing the foot and lower limb biomechanics.
